Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a hot topic! AI is creating a closer relationship between the patient and provider through decision support systems, patient surveys, and image analysis (Cleveland Clinic, 2018). The applications of AI in healthcare analytics are numerous and diverse.
Leveraging data, AI can add major benefits to decision support systems (DSS) as demonstrated in Humber River’s command center. As we transition from volume to value based care, AI will aid in reducing medical errors, avoid duplicate testing and minimize hospital admission (Ofri,2016). Consequently, this will improve workflow and alerts. Additionally, AI can provide valuable treatment suggestions for doctors.
Another promising aspect of AI lies in its ability to triage patients, resulting in faster diagnoses and improved workflow. The FDA has recently approved AI software AIDoc, Zebra Medical, and MaxQ which aid in the detection of cerebral hemorrhage bleeds. The FDA is quick to approve the triage workflow applications but this doesn’t change the basic role of a clinician (Weisberg et al., 2020, p. 363).
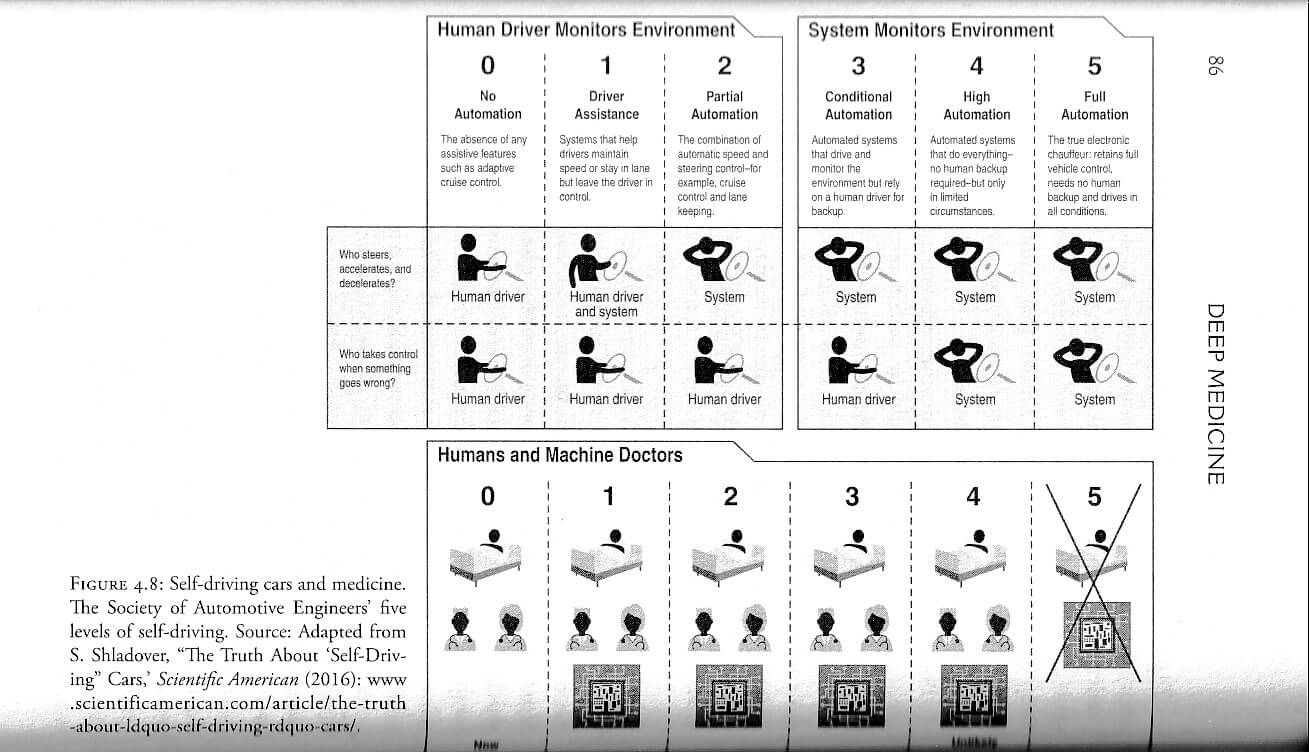
AI helps augment image analysis for diagnosis. Artificial intelligence can ingest a greater amount of data than a radiologist with years of experience (Hosny et al., 2018). In AI, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) find hidden layers in images to find patterns. These machines are usually trained with labeled data. The promise of AI comes with a fear that humans will be displaced. While the potential of AI is promising, concerns arise regarding the potential displacement of human professionals. Nevertheless, the ultimate decision-making authority will always remain with the clinician. Unlike AI being used in creating art or games, a completely automated AI system in healthcare won’t be tolerated because of the premium we place on our health (Topol, 2019, p. 87).
References
Cleveland Clinic. (2018, November 30). MIS2018: “Top 10” Medical Innovations: 2019 [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=2699&v=yVIbfQFlPv0&feature=emb_logo
Hosny, A., Parmar, C., Quackenbush, J., Schwartz, L., & Aerts, H. (2018). Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat Rev Cancer, 500-510. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-018-0016-5
Ofri, K. (2016, October 14). Four ways clinical decision support can improve outcomes. Managed HealthCare Executive. Retrieved August 30, 2020, from https://www.managedhealthcareexecutive.com/view/four-ways-clinical-decision-support-can-improve-outcomes
Topol, Eric J. Deep Medicine : How Artificial Intelligence Can Make Healthcare Human Again Eric Topol. First edition. New York: Basic Books, 2019. Print.
Weisberg, E. M., Chu, L. C., Fishman, E. K. (2020). The first use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the ER: triage not diagnosis. Emergency Radiology, 27(4), 361-366.
